Hey there! Have you ever wondered about the potential side effects of supplements? You know, those little pills and powders that promise to improve your health and well-being? Well, in this article, we’re going to dive into that very topic. We’ll take a closer look at what supplements are, why people use them, and most importantly, the potential side effects you should be aware of. So, if you’re curious about whether supplements are really as safe and effective as they claim to be, stick around because we’ve got all the information you need!
Now, you might be thinking, “Well, I’ve been taking supplements for a while now and haven’t experienced any side effects.” That’s great! However, it’s important to understand that not everyone reacts the same way to supplements. And while most supplements are generally safe when taken as directed, there are still potential side effects that can occur. In this article, we’ll discuss some of the most common side effects associated with supplements, such as digestive issues, allergic reactions, and interactions with medications. So, whether you’re currently taking supplements or considering adding them to your routine, this article will provide you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Supplements have become increasingly popular in recent years, with many people turning to them to fill nutritional gaps and support their overall health. While supplements can offer a range of benefits, it is important to understand the potential side effects that can accompany their use. In this article, we will explore the various types of supplements and their associated side effects, as well as factors that can increase the risk of experiencing negative effects. Additionally, we will discuss how to recognize and manage side effects, the importance of proper usage, and steps to ensure supplement safety. Finally, we will examine the role of education and awareness in reducing the incidence of side effects and conclude with key takeaways.
This image is property of media.defense.gov.
1. Understanding Supplements
1.1 What Are Supplements?
Supplements are formulated products that contain vitamins, minerals, herbs, or other dietary ingredients. They are intended to supplement the diet and provide additional nutrients that may be lacking. Supplements come in various forms, including pills, capsules, powders, and liquids.
1.2 Types of Supplements
There are several types of supplements available on the market. Some common categories include vitamin supplements, mineral supplements, herbal supplements, and protein supplements. Each type serves a different purpose and provides specific nutrients to support various bodily functions.
1.3 Why Do People Take Supplements?
People take supplements for a variety of reasons, including addressing nutrient deficiencies, supporting overall health, enhancing physical performance, and managing specific health conditions. However, it is important to note that supplements should not be used as a replacement for a balanced diet.
1.4 How Are Supplements Regulated?
The regulation of supplements varies from country to country. In the United States, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA). However, unlike medications, supplements are not required to undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before they are marketed.
2. Exploring Potential Side Effects
2.1 Definition of Side Effects
Side effects are unintended or adverse reactions that can occur when taking supplements. These effects can vary in severity and may include mild discomfort, allergic reactions, or more serious complications.
2.2 Common Side Effects of Supplements
Some supplements can cause common side effects such as gastrointestinal upset, nausea, diarrhea, or constipation. These effects are typically mild and resolve on their own. However, they can still be bothersome and impact an individual’s overall well-being.
2.3 Rare and Serious Side Effects
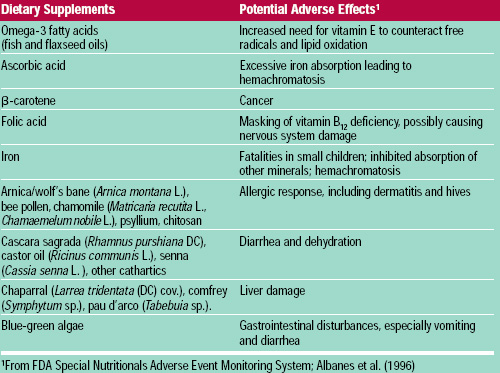
While rare, some supplements can cause serious side effects. For example, high doses of certain vitamins or minerals can lead to toxicity. Additionally, some herbal supplements may interact with medications, resulting in adverse effects. It is important to be aware of these potential risks and consult a healthcare professional if any concerning symptoms occur.
2.4 Factors Influencing Side Effects
Several factors can influence the likelihood and severity of side effects from supplements. These include the dosage and duration of use, interactions with other medications or supplements, underlying medical conditions, and individual susceptibility. It is important to consider these factors when deciding to take supplements and when monitoring for potential side effects.
This image is property of www.verywellhealth.com.
3. Factors Increasing Risk
3.1 Dosage and Duration
The dosage and duration of supplement use can significantly impact the risk of experiencing side effects. Taking higher than recommended doses or using supplements for an extended period can increase the likelihood of adverse reactions.
3.2 Interactions with Other Supplements or Medications
Supplements can interact with other medications or supplements, resulting in unwanted effects. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all the supplements and medications you are taking to avoid potential interactions.
3.3 Underlying Medical Conditions
Individuals with certain underlying medical conditions may be more susceptible to experiencing side effects from supplements. Chronic diseases, liver or kidney disorders, and allergies can increase the risk of adverse reactions.
3.4 Allergic Reactions
Some supplements may contain allergens, such as soy, gluten, or shellfish derivatives. Individuals with known allergies should carefully read product labels and consult with their healthcare provider to avoid potential allergic reactions.
4. Specific Supplements and Their Side Effects
4.1 Vitamin Supplements
Vitamin supplements are widely used to address deficiencies, support immune function, or promote healthy hair, skin, and nails. However, excessive intake of certain vitamins, such as vitamin A or vitamin D, can lead to toxicity and cause symptoms like nausea, headaches, or even organ damage.
4.2 Mineral Supplements
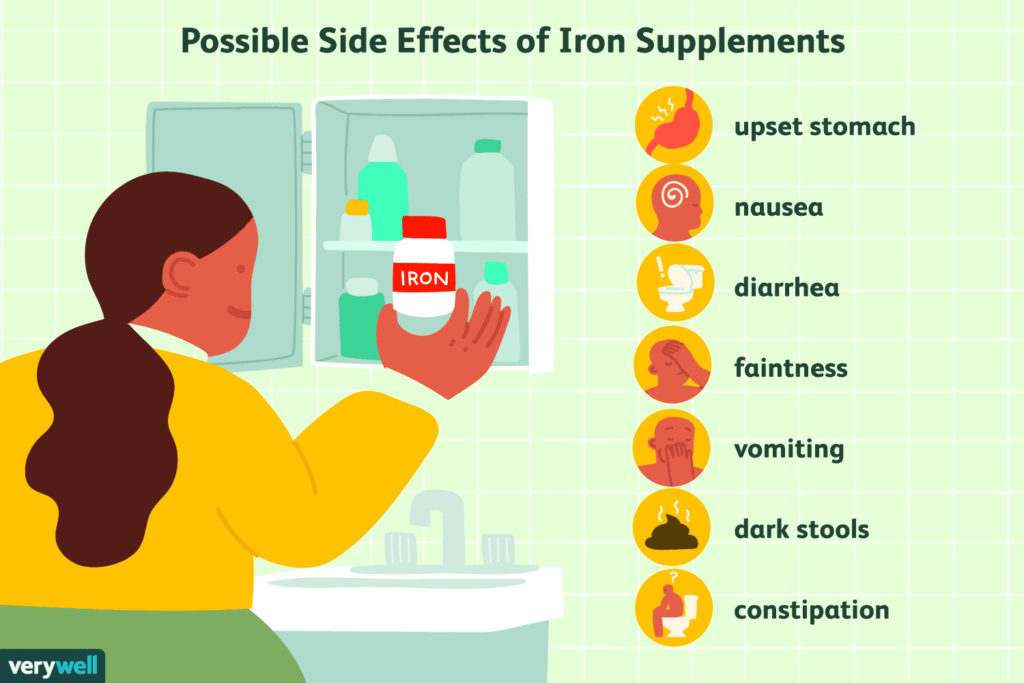
Mineral supplements, such as iron or calcium, are often taken to address deficiencies or support bone health. However, high doses of certain minerals can cause gastrointestinal discomfort, constipation, or even interfere with the absorption of other nutrients.
4.3 Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements can have powerful effects on the body, but they also carry the risk of side effects. For example, St. John’s wort, a commonly used herbal supplement for mood support, can interact with certain medications and lead to adverse reactions.
4.4 Protein Supplements
Protein supplements, popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts, are generally safe. However, excessive protein intake can burden the kidneys and may cause digestive issues like bloating or stomach cramps.

This image is property of manoxblog.com.
5. Recognizing and Managing Side Effects
5.1 Identifying Side Effects
Recognizing the signs of side effects is crucial for managing their impact. It is important to be vigilant for any physical or emotional changes that occur after starting a new supplement regimen.
5.2 When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience severe or persistent side effects, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance, evaluate your symptoms, and recommend necessary interventions or adjustments to your supplement routine.
5.3 Managing and Treating Side Effects
Managing side effects may involve adjusting the dosage, changing the timing of supplementation, or discontinuing the use of certain supplements. Mild gastrointestinal issues can often be managed with dietary modifications, such as consuming supplements with food.
5.4 Prevention Strategies
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is important to start with the lowest effective dose of a supplement and gradually increase if needed. Additionally, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and duration guidelines provided by healthcare professionals or product labels.
6. Importance of Proper Usage
6.1 Following Recommended Dosages
Following recommended dosages is essential for supplement safety. Taking more than the recommended amount does not necessarily provide additional benefits and can increase the risk of side effects.
6.2 Adhering to Instructions
Adhering to the instructions provided by the manufacturer or healthcare professional is crucial for safe and effective supplement use. This includes taking supplements at the recommended time and with appropriate dietary considerations.
6.3 Consulting Experts or Professionals
If you are unsure about the appropriate supplements for your individual needs or have concerns regarding potential side effects, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian. They can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific health condition and goals.
6.4 Monitoring Side Effects
Regularly monitoring any potential side effects is essential to ensure the ongoing safety and effectiveness of your supplement regimen. If you notice any new or concerning symptoms, it is important to promptly address them with your healthcare provider.
This image is property of www.ift.org.
7. Ensuring Supplement Safety
7.1 Quality and Approval
When selecting supplements, it is important to choose products from reputable manufacturers that adhere to strict quality control standards. Look for certifications or seals indicating third-party testing and quality assurance.
7.2 Researching Brands and Manufacturers
Researching the reputation and track record of supplement brands and manufacturers can provide important insights into their commitment to safety and product quality.
7.3 Checking for Third-Party Testing
Third-party testing helps ensure that supplements contain the ingredients listed on the label and are free from contaminants. Look for supplements that have undergone independent testing and have the appropriate certifications.
7.4 Reporting Adverse Effects
If you experience any adverse effects from a supplement, it is important to report it to the appropriate authorities. In the United States, the FDA has the MedWatch program where consumers can submit reports on adverse reactions to dietary supplements.
8. Education and Awareness
8.1 Promoting Public Knowledge
It is crucial to promote public knowledge about the potential side effects of supplements. This includes providing accessible and evidence-based information to help individuals make informed decisions about their supplement use.
8.2 Educating Consumers on Risks
Consumer education campaigns should focus on raising awareness about potential risks and side effects associated with supplements. This can help individuals make more informed choices and understand the importance of consulting healthcare professionals.
8.3 Encouraging Informed Decisions
Encouraging individuals to gather information, consult healthcare professionals, and carefully consider their personal health goals and needs before starting any supplement regimen is key to minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
8.4 Raising Awareness about Side Effects
Raising awareness about the potential side effects of supplements among both consumers and healthcare professionals can contribute to more effective management and prevention strategies.

This image is property of cdn2.stylecraze.com.
9. Reducing Side Effect Incidences
9.1 Regulating Supplement Industry
Regulating the supplement industry more strictly can help ensure the safety and quality of products. Implementing stricter guidelines for testing, labeling, and claims can reduce the risk of side effects and misleading information.
9.2 Strengthening Manufacturing Standards
Strengthening manufacturing standards can help prevent contamination and mislabeling of supplements. This includes ensuring adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and frequent inspections of manufacturing facilities.
9.3 Monitoring and Surveillance
Regular monitoring and surveillance of the supplement market can help identify problematic products and detect emerging safety concerns. This allows for timely intervention and consumer protection.
9.4 Collaborating with Healthcare Providers
Collaboration between supplement manufacturers, regulators, and healthcare providers can facilitate the exchange of information, enhance safety monitoring, and improve the overall management of supplement-related side effects.
10. Conclusion
Supplements can provide important nutritional support, but it is crucial to be aware of their potential side effects. Understanding the different types of supplements, factors that can increase the risk of side effects, and how to recognize, manage, and prevent adverse effects are all vital for safe and effective supplement use. By prioritizing education, awareness, and safety measures, we can work towards reducing the incidence of side effects and promoting the responsible use of supplements for optimal health.